Psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis are both common skin conditions that can cause lots of symptoms and affect your self esteem. You need to understand the differences between them in order to administer the appropriate treatment and manage the symptoms effectively.
In a nutshell, psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that leads to an overproduction of skin cells, while seborrheic dermatitis is caused by your immune system’s hyper-reactive response to Malassezia and its byproducts. There is an overlap of treatments that are effective for both but psoriasis is a serious disease needing more aggressive medical treatment.
Let’s take a deep dive:
- Understanding Psoriasis and Seborrheic Dermatitis
- How to tell the difference between seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis?
- Scalp Psoriasis versus Scalp Seb Derm
- Is seborrheic dermatitis linked to psoriasis?
- Is it possible to have both psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis?
- What is Sebopsoriasis?
- Can you treat both seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis at the same time?
Understanding Psoriasis and Seborrheic Dermatitis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease characterized by the presence of raised, red, scaly patches known as plaques. The condition results from an overactive immune system, causing accelerated skin cell growth and inflammation. Plaques can appear anywhere on the skin, but they are typically found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Psoriasis can be itchy and sometimes painful.
There are actually a few types of proriasis – plaque, guttate, pustular, inverse and erythrodermic psoriasis. Of all these types of psoriasis, the most common and the one most likely to be confused with Seb Derm is plaque psoriasis. Throughout the rest of this article, whenever I refer to psoriasis, I mean plaque psoriasis.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin condition characterized by greasy yellow or slightly red scaly patches, and dandruff. Unlike psoriasis, the primary areas affected by seborrheic dermatitis are the oily parts of the skin, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. The exact cause of this condition remains unclear, but it is believed to be related to an overgrowth of yeast, environmental factors, or a genetic predisposition.
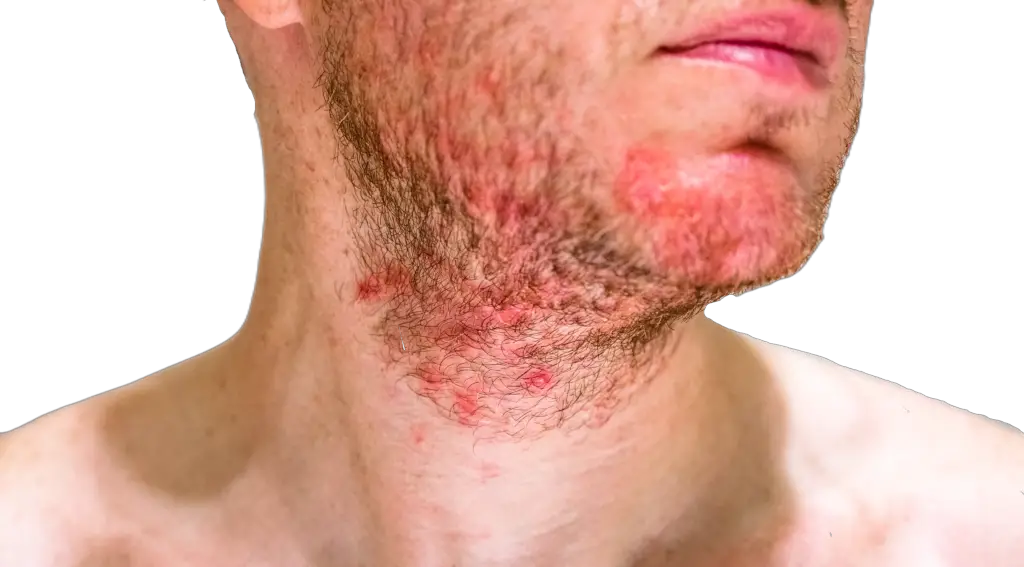
Here is a quick comparison of the two conditions:
| Psoriasis | Seborrheic Dermatitis |
|---|---|
| Raised, red, scaly plaques, silvery scale | Greasy, yellow or red patches, sometimes scaly |
| Often found on elbows, knees & scalp | Affects oily parts of skin, like scalp & face |
| Caused by overactive immune system | Caused by a hypersensitivity to Malassezia |
| Can affect the nails and joints | Doesn’t usually affect other organs |
Recognizing the differences between psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis is essential for proper treatment and management of your skin health. If you suspect that you may have one of these conditions, consult your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Remember that managing your skin condition is an ongoing process, and finding a treatment that works for you may take some time and patience.
How to tell the difference between seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis?
Generally, it’s pretty easy to differentiate between the two conditions. Psoriasis typically has a characteristic red and raised plaque with a well-defined border. It can often be covered by a silvery scale. The plaques have a predilection for the extensor aspects of the body, such as elbows, knees, and lower back.
You don’t often find Seb Derm rash in these areas.
On the other hand, seborrheic dermatitis is usually characterized by greasy, yellow patches on the scalp, face, neck, upper chest and upper back, where most of your oil glands are. Seb Derm rashes are usually not raised (unless it’s uber inflammed, which happened to me after exposing it to the sun – long story. Read about it here) but can look a bit red.
In addition to skin manifestations, psoriasis can also present with non-cutaneous symptoms, including psoriatic arthritis, which is an inflammatory arthritis associated with joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. It may also cause nail changes, such as pitting, thickening, or separation from the nail bed.
Seb Derm rarely can affect the eyes but not typically other parts of your body.
Scalp Psoriasis versus Scalp Seb Derm
Even though both psoriasis and Seb Derm pretty much keep to their own territories, they can both affect the scalp. That’s where most of the confusion occurs.
When psoriasis affects the scalp, you will see the same red inflamed patches with white or silver scales on your scalp. These plaques look thick and raised, and may extend beyond the hairline. You may also see red bumpy patches.
Seb Derm of the scalp usually results in itch and dandruff. In more severe Seb Derm, you may see crusts and red, inflammed skin.
Both scalp psoriasis and Seb Derm can cause itchiness and flaking that can be hard to differentiate.
My expert advice?
See your healthcare provider or dermatologist to get a medical diagnosis.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may need to perform additional tests like a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. During this procedure, a small sample of the affected skin is removed and examined under a microscope.
Is seborrheic dermatitis linked to psoriasis?
While seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis can appear similar, they are not inherently linked. They are distinct skin conditions. However, both conditions may share similar genetic and immune system factors.
Is it possible to have both psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis?
Yes, unfortunately it’s possible to have both psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis. Some people are unfortunate enough to have both skin conditions at the same time, or they can occur different times in their lives.
You may also have a combined form of both skin disorders – sebopsoriasis.
What is Sebopsoriasis?
Sebopsoriasis is a skin condition that combines symptoms of both seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis. It’s an overlap between these two separate conditions, in which features of both conditions coexist.
Sebopsoriasis often presents as a red or purple rash with yellow, greasy scales, typically appearing within skin folds and on the face, scalp, and other areas. Some dermatologists consider sebopsoriasis a transitional condition between scalp psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis, rather than a distinct condition.
Can you treat both seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis at the same time?
There are actually a few treatments that work for both seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Medicated shampoos
Medicated shampoos containing ingredients like coal tar, salicylic acid, or ketoconazole can be helpful for your scalp. They can alleviate symptoms such as itchiness and control the growth of the skin cells. Gently massage them into your scalp and leave on for a few minutes before rinsing thoroughly. Check it out on Amazon
Check it out on Amazon
Topical steroids
Long-term readers know I hate steroid creams but yes, corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone can relieve symptoms for both conditions by reducing local inflammation.
Phototherapy
This therapeutic method involves the use of ultraviolet (UV) light to slow down the growth of skin cells. I have no experience with using UV light on Seb Derm and it’s not something you should DIY at home. Speak with your healthcare provider about the suitability of this treatment for your specific case.
And my all time favourite:
Healthy Lifestyle Changes
Your skin reflects your inner health. Skin disorders are never skin-deep. You can use all the topical treatments you want but it’s like putting a band-aid on a gaping wound. You need to heal from within as well.
Stress worsens both conditions and lead to flare-ups. Incorporate stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or regular exercise into your daily routine.
Adopt a healthy, balanced diet. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins support overall skin health and a healthy immune system.
This is where the combined treatment for both Seb Derm and psoriasis ends. Psoriasis is a distinct disease, very different from Seb Derm and requires more aggressive medical treatment. By all means, do your Google search. Then, seek help from your doctor.
If you think you may have eczema, read about the differences between eczema and Seb Derm in this article.
 Check it out on Amazon
Check it out on Amazon
Pingback: seborrheic dermatitis beard